Jetpack Compose, the modern Android UI toolkit, has revolutionized the way we build user interfaces in Android apps. With its declarative approach and powerful components, creating complex UIs has become simpler and more efficient. In this blog post, we will dive deep into one of Jetpack Compose’s versatile components – LazyRow. We’ll explore its features, benefits, and provide a practical example.
What is LazyRow?
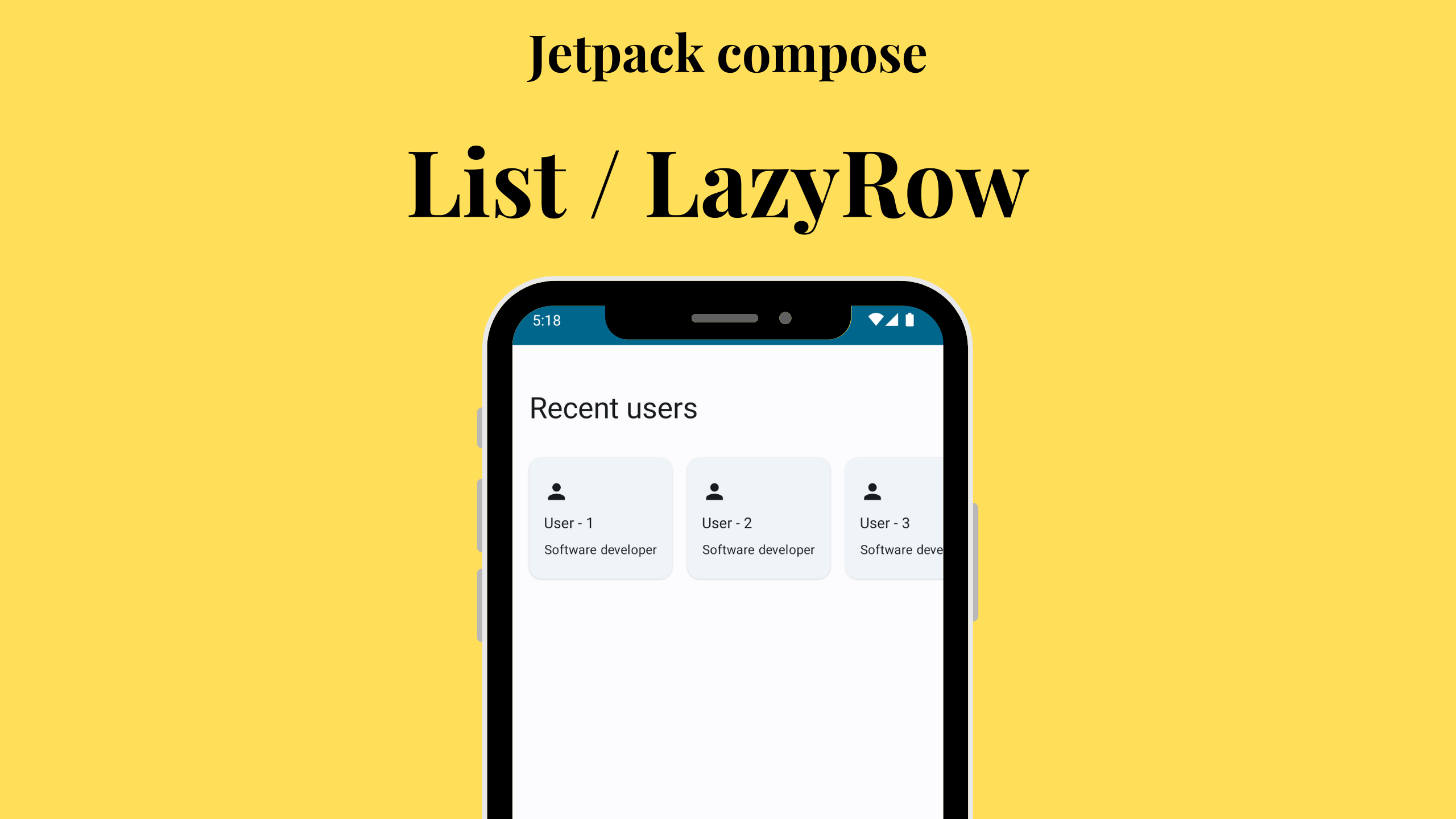
LazyRow is a horizontal scrolling list component in Jetpack Compose. It’s designed to efficiently render and display a list of items, particularly when the list contains a large number of elements. Unlike traditional RecyclerView, LazyRow only composes and lays out the items that are currently visible on the screen, which makes it highly performant for long lists.
The Anatomy of a LazyRow
Before we explore the code example you provided, let’s break down the key components of a LazyRow:
items: This is where you specify the data you want to display in yourLazyRow. It’s essentially a mapping of your data to composables. In your code, you have a list of integers from 1 to 10 as your data.horizontalArrangement: This parameter defines how the items are arranged horizontally. In your example, you’re usingArrangement.spacedBy(14.dp), which adds space between items.contentPadding: This defines the padding for the entireLazyRow.
A Practical Example
Let’s dissect the code you provided:
@Composable
fun ListDemoLazyRow() {
Column {
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(40.dp))
Text(
modifier = Modifier.padding(horizontal = 16.dp),
text = "Recent users",
style = MaterialTheme.typography.headlineMedium,
textAlign = TextAlign.Start,
)
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(30.dp))
LazyRow(
modifier = Modifier,
contentPadding = PaddingValues(horizontal = 16.dp),
horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.spacedBy(14.dp)
) {
items(items = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10)) { item ->
ElevatedCard(modifier = Modifier.clickable { }) {
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.clickable { }
.padding(horizontal = 14.dp, vertical = 20.dp),
) {
Icon(
imageVector = Icons.Default.Person,
contentDescription = "Person"
)
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(8.dp))
Text(
modifier = Modifier,
text = "User - $item",
style = MaterialTheme.typography.bodyMedium,
textAlign = TextAlign.Start,
)
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(8.dp))
Text(
modifier = Modifier,
text = "Software developer",
style = MaterialTheme.typography.bodySmall,
textAlign = TextAlign.Start,
)
}
}
}
}
}
}In this code, we have a LazyRow inside a Column. The LazyRow displays a list of recent users, each represented by a card. Here’s a quick overview of what’s happening:
- The
Columnis used to structure the content, with appropriate spacing and text elements. Spacerelements are used for creating vertical spacing.- The
Textcomposable displays a title for the section. - Inside the
LazyRow, theitemsfunction maps the list of integers to a series ofElevatedCardcomposables. - Each card contains a
Columnwith anIcon, user details, and a role description.
Customization and Interaction
In your example, you’ve also included Modifier.clickable{} to make the cards interactive. This allows you to respond to user actions like clicks, which can be useful for navigation or showing more details about a user.
Wrapping up
LazyRow is a powerful component in Jetpack Compose that simplifies the creation of horizontal scrolling lists with excellent performance. It’s particularly handy when dealing with large datasets. In this blog post, we explored its features and saw how it can be used to create a list of recent users. Jetpack Compose continues to make Android app development more efficient, intuitive, and enjoyable.
Happy composing!

Leave a Reply